AI and the Evolution of Power Electronics

The invention of mercury Arc valves in the early 1900s was considered a revolution in itself due to the numerous applications it might serve in the industry. With the development of power semiconductor devices such as BJT, the market segment saw greater power efficiency and performance, as well as lower manufacturing costs for power electronic systems. Technological improvements in semiconductor-based power devices have occurred, with the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in the entire power electronics system.
Practically every industrial automation application, whether for generation or transmission, uses power electronics. Renewable energy generation, high-voltage direct current (HVDC) power transmission, flexible AC transmission systems, electric cars, and microgrids are just a few of the applications that semiconductor-based power devices enable. However, as the industry evolves, so does the demand for more efficient manufacturing, control, and maintenance of these components. Semiconductor-based power devices are high-frequency devices with high switching frequencies, making control difficult. Silicon Carbide (SiC) based JFETs and MOSFETs are one example. Artificial intelligence has proven to be an efficient method of designing, controlling, and sustaining power electrical systems.
AI and Power Electronics
Intelligence is no longer a human characteristic. Industry 3.0’s lack of automation and intelligent systems has made AI and ML the foundation of Industry 4.0. The goal of AI is to enable robots to display human-like thinking and intellect, with the sole difference being that these machines will be able to think as efficiently as humans without tiring. Face recognition, driverless vehicles, speech recognition, chatbots, and other industries benefit from AI.
AI provides special implementation advantages in power electronics because of specific constraints such as rapid tuning speed and high sensitivity in condition monitoring. AI has applications in three phases of the power electronics life cycle: design, control, and maintenance.
With advancements in IoT and Big data analytics, a vast amount of data is now available to feed the AI algorithms that monitor power electronics throughout their life cycle.
The growing volume of data provides a solid foundation for the advancement of artificial intelligence in power electronics. AI may use data to increase product competitiveness through global design optimization, intelligent control, system health status estimate, and so on. It is useful to conduct power electronics research from a data-driven perspective as a result, especially in challenging and complex application instances.
AI in Power Electronics: Function and Methods
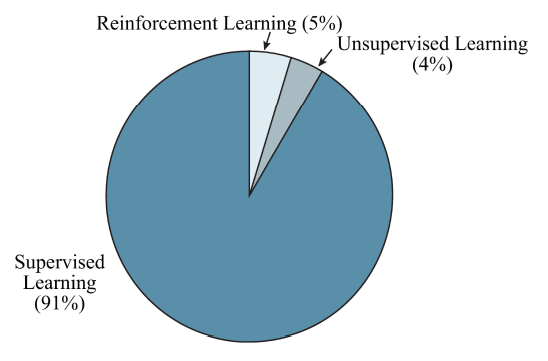
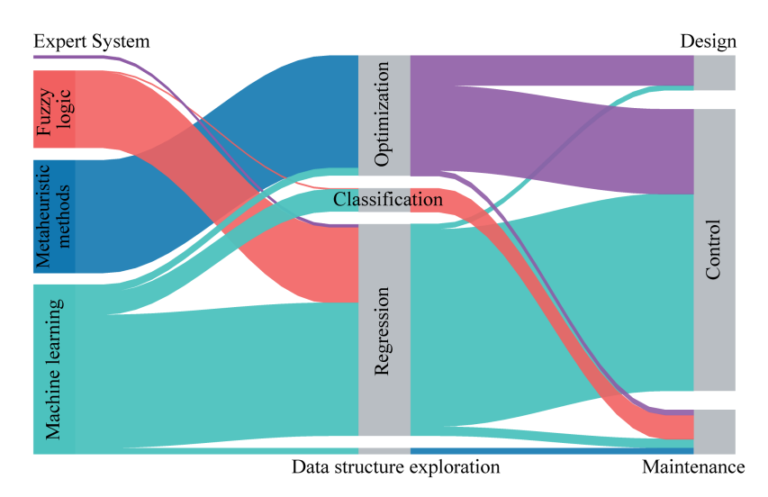
Artificial intelligence is most prevalent in power electronics during the control phase, followed by the maintenance phase, and least prevalent during the design phase. The AI functions employed can be broadly classified as optimization, classification, regression, and data structure exploration, with regression and optimization accounting for the vast bulk of tasks. The most often used artificial intelligence techniques in power electronics include expert systems, fuzzy logic, metaheuristic methods, and machine learning. Machine learning accounts for the vast bulk of power electronic applications. For use in power electronics, ML is further classified as supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforced learning.
Expert systems and fuzzy logic have limited applications at the moment, especially fuzzy logic, but as more potent computing units become accessible, more sophisticated AI tools are being used. Power electronics use metaheuristic methods, which are continually evolving. They can be used independently or in combination with other machine-learning algorithms to finish a task. The current machine learning algorithm frontier in power electronics, RL, was made possible by the swift advancement of computer technology.
AI’s potential in power electronics in the future
Despite extensive literature review and study on the potential application of AI in power electronics, it has yet to realize its full potential. Training AI models for deeper improved optimization requires deeper research and analysis.
There are various reasons why industries are hesitant to use AI. Some examples are:
1) Implementation complexity
2) Concerns about algorithm reliability and accuracy
3) Additional hardware costs
4) Significant computational energy usage
Another impediment to AI implementation in power electronics is the scarcity of large datasets on which to train models. However, the available datasets are limited since producing these datasets takes time, and the available data for safety-critical procedures is substantially smaller. As a result, developing a data-light AI system that can give desired solutions with minimal training data is necessary.
It is also vital to develop understandable AI algorithms that would convince professionals to use them in safety-critical applications. Understanding how the model operates will aid in improving its characteristics for the desired implementation. Industry 4.0, which will use autonomous machines to create smart factories, has established AI and ML as its cornerstone. Power electronics and artificial intelligence (AI) are two incredibly strong technologies with the potential to change the world. Although there are hurdles to implementing AI with power electronics, it should not be a far-fetched goal with extensive research.
References
[1] S. Zhao, F. Blaabjerg and H. Wang, ” An Overview of Artificial Intelligence Applications for
Power Electronics,” in IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, vol. 36, no. 4, pp. 4633-4658,
April 2021, doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2020.3024914.